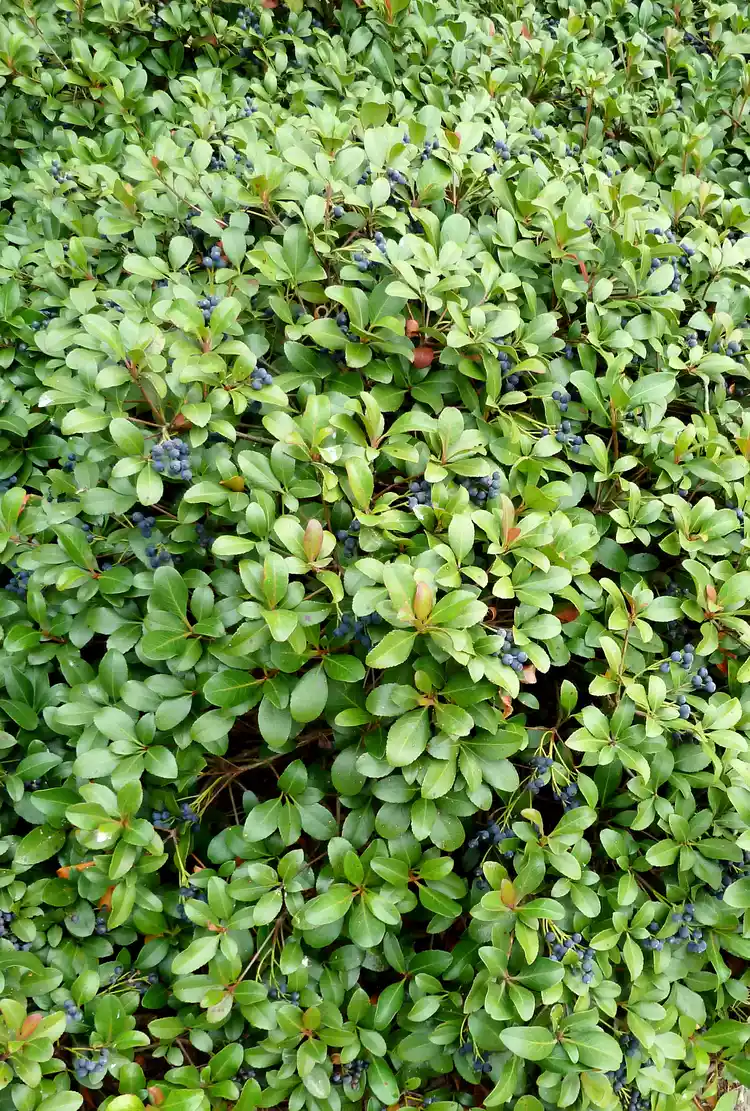
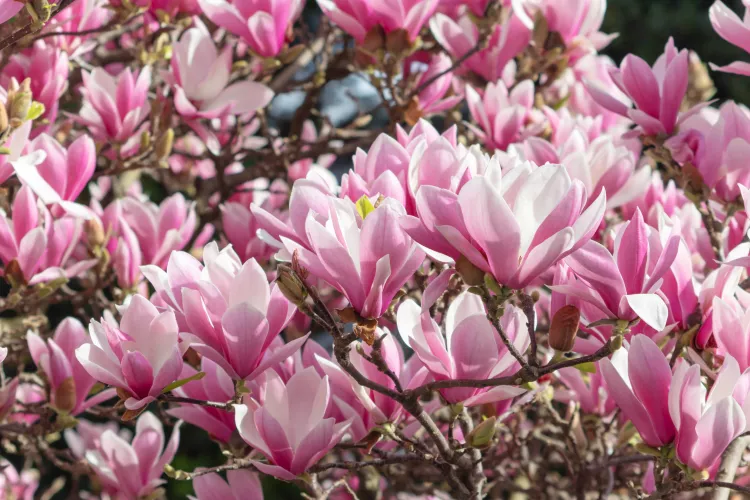
Native to Southeast Asia, Indian hawthorn is a broadleaf evergreen shrub that offers soft pink flowers in spring. Bluish-purple fruits follow, providing winter sustenance to birds and small mammals. Slow-growing Indian hawthorn requires minimal pruning, and the variety of selections available makes it easy to find the right-sized plant to suit your space. It's also drought tolerant once established. This shrub is relatively cold-tolerant (USDA Hardiness Zone 8) and is worth consideration in a protected location in Zone 7. Here's what you need to know to successfully grow Indian hawthorn in your garden.
Indian Hawthorn Overview
| Genus Name | Raphiolepis spp. |
| Common Name | Indian Hawthorn |
| Plant Type | Shrub |
| Light | Sun |
| Height | 2 to 6 feet |
| Width | 3 to 6 feet |
| Flower Color | Pink, White |
| Foliage Color | Blue/Green |
| Season Features | Reblooming, Spring Bloom, Summer Bloom |
| Special Features | Low Maintenance |
| Zones | 10, 8, 9 |
| Propagation | Seed, Stem Cuttings |
| Problem Solvers | Drought Tolerant |
Where to Plant Indian Hawthorn
Plant Indian hawthorn in a well-drained, full-sun location. Space plants to allow them to grow to their mature size without aggressive pruning. Proper spacing will improve air circulation around the plant, which is imperative to grow this shrub successfully. Sunlight and airflow quickly dry moisture off the leaves. Moisture on the leaves can lead to leaf spot disease, which can severely damage your plants.
The mature size of an Indian hawthorn shrub varies based on the selection. Smaller varieties work well to line a formal walkway or as small evergreens at the front of a mixed border, while larger selections make excellent foundation plants. An individual specimen will make a lovely focal point in the landscape or contribute nicely to a mixed garden border.
How and When to Plant Indian Hawthorn
Dig a hole no deeper than the plant's root ball, loosen the surrounding soil to facilitate root growth, and place the plant at the same depth as it was in its nursery container. Backfill around the plant with soil you removed from the hole, then water deeply and regularly until the plant has established new roots.
In heavy soils, or if excess moisture is a threat, plant Indian hawthorn shrubs with a fourth of the root ball out of the ground, grading the existing soil to the top of the root ball. This will improve drainage away from the plant and mitigate the potential for root rot.
In warm climates that do not receive an annual frost, Indian hawthorn can be planted in late autumn through spring. Avoid planting in late spring to allow the plant to become established before the summer heat. In cooler regions, install plants in spring to allow them to settle in and develop a healthy root system before winter.
Indian Hawthorn Care Tips
Indian hawthorn is easy to grow, provided it receives adequate moisture, good air circulation, and full sun. Most problems with Indian hawthorn are minimized by good site selection, proper planting, and correct watering.
Light
This shrub requires full sun to thrive. It is prone to leaf spot disease in shady conditions where water does not evaporate off the leaf as quickly as in full sun.
Soil and Water
Indian hawthorn grows best in average, well-drained garden soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. Most garden soils are between 6.0 and 7.0.
Established plants are drought tolerant, but Indian hawthorn will perform best in soils that receive regular moisture. Be careful when watering your plants–moisture on the leaves can spread diseases that will quickly infect neighboring plants. To avoid overhead watering, use soaker hoses or small sprinklers with the water flow reduced enough that it does not land on the leaves. Water early in the day so that the sun can dry off any residual moisture that makes its way to the surface of the leaves. This is especially important for plants that do not receive full sun or good air circulation.
As with all broadleaf evergreens, it is vital that Indian hawthorn does not completely dry out during the cold winter months. Winter winds can desiccate the plant, and it will not recover come spring. Check the soil around your plants regularly and water as needed, usually no more than 1-2 times monthly.
Temperature and Humidity
Indian hawthorn will thrive in warm temperatures with low to moderate humidity. In humid regions, ensure that your plant has good air circulation and full sunlight. This shrub is hardy to about 10°F, possibly colder, but may experience tip dieback at these lower temperatures. If you experience dieback, simply prune the damaged stems back to live growth in spring.
Fertilizer
This plant requires minimal fertilizer if grown in average to fertile garden soil. Apply fertilizer once each spring. Use a balanced (10-10-10 or 20-20-20) granular fertilizer, and follow the application rates listed on the container. Overapplication of fertilizer can cause excessive growth that is prone to disease.
Plants grown in containers will need additional fertilizer throughout the season due to nutrients leaching out of the growing mix. Apply a slow-release granular fertilizer at the beginning of the spring growing season and then again in mid-summer.
Pruning
Indian hawthorn grows naturally as a rounded shrub and requires little pruning. However, plants can be sheared to maintain a uniform and formal appearance. Deadheading is unnecessary and, if done, will stop the plant from developing the dark purple berries favored by wildlife.
Flower buds are formed on old wood. Limit pruning until immediately after spring flowering to maximize the floral display. Avoid pruning your plants from late summer through autumn in regions where you may receive a frost. Newly developed leaves will not have time to harden off, and will be damaged by the onslaught of cold weather.
Large mature specimens can be limbed up to expose the trunks, creating a small multi-stemmed tree. Remove new growth from the stems to maintain this appearance.
Hard regenerative pruning should occur early in the growing season to allow the plant time to regrow before winter.
Potting and Repotting Indian Hawthorn
Indian hawthorn grows best when planted directly in the ground but will perform well in a planter if the soil drains and does not remain soggy. Ensure that your planter has adequate drainage holes. Containers placed directly on the ground may not drain efficiently. Use commercially available pot risers, stones, bricks, or cut pieces of lumber to elevate the pot off the ground at least a half an inch. This allows water to easily drain from the bottom of the planter and will also help eliminate staining on your hardscape.
Containers should be larger than the root ball of your plant, but not so much so that the plant is out of scale to the pot. A container 6-12 inches wider than the root ball of your plant will allow room for the roots to grow without holding too much moisture, which can cause the plant to rot. Check the plant at the beginning and end of each season, and repot in late winter or early spring if the plant has outgrown the container. Follow the same watering rules with container-grown plants. Keep the soil moist but not saturated, and do not water the leaves of the plant.
Pests and Problems
Several common plant diseases afflict Indian hawthorn, although the damage can be mitigated with appropriate care throughout the season.
Entomosporium leaf spot causes small red or brown spots on the tops of the leaves, which slowly enlarge as the leaf matures. The leaf will also develop a reddish color. In extreme cases, the plant will completely lose its leaves. Rake up and remove all infected debris, increase airflow around the plant, and avoid overhead watering to manage the issue.
Fire blight may appear in late spring and spread quickly through new growth. Early signs of fire blight include dark streaks on the stems and branches of the plant, complete with oozing cankers. You will also notice that the flowers may wither and die, and the leaves will turn black and fall off the plant. Treat fire blight by removing infected plant sections, improving air circulation, and avoiding overhead watering. Contact your local county extension agent for advice regarding chemical treatments suitable for your location.
How to Propagate Indian Hawthorn
Take semi-hardwood cuttings from July through August, dip in rooting hormone, and plant in damp (not saturated) well-drained potting soil. Cuttings should be placed in a shady location under a mist system or covered with a plastic vessel and hand-misted twice daily until rooting occurs.
Alternatively, collect Indian hawthorn seeds in winter and remove the fleshy pulp. Sow a fourth-inch deep into pots. Store the pots in a cool greenhouse until germination occurs. Do not allow the potting mix to dry out completely, but refrain from overwatering the soil
Types of Indian Hawthorn
‘Indian Princess’ Indian Hawthorn
‘Indian Princess’ is a popular compact form of Indian hawthorn that develops into a 3-foot-tall by 5-foot-wide mound with pink flowers that fade to white as the season progresses.
‘Ballerina’ Indian Hawthorn
This small selection of Indian hawthorn is only 2 to 3 feet tall and 3 to 4 feet wide at maturity. The pale pink flowers bloom in spring and often rebloom later.
‘Pink Lady’ Indian Hawthorn
‘Pink Lady’ is a fast-growing selection, reaching 6 feet tall and up to 6 feet wide. The pink flowers bloom over a long period. It is reportedly resistant to leaf spot disease.
Indian Hawthorn Companion Plants
Crape Myrtle
Crape myrtles (Lagerstroemia spp.) range from small shrubs to 20-foot-tall multi-stemmed trees. The colors range from white to pink to fuchsia and even brick red. Tree-form selections often have attractive smooth bark. Crape myrtle blooms in mid-late summer and can be used to extend the flowering season in your garden.
Lantana
Lantana performs best in hot weather and is available in various colors. Use lantana as a seasonal annual or perennial where hardy to provide an additional pop of color against the backdrop of evergreen Indian hawthorn.
Dusty Miller
The silver foliage of dusty miller pops against the dark green leaves of Indian hawthorn. Grow dusty miller as a warm season annual or as a perennial in Hardiness Zones 7-10.