Leafhoppers may look kind of cute (for a bug), and some types even sport bright colors and striking patterns. But these insects can feed on a lot of different garden plants and even spread diseases to your crops. The good news is that leafhoppers are easy to control, as long as you act quickly when you spot these bugs in your garden. These pests can rapidly reproduce and cause significant damage to vegetables, fruit, flowers and herbs in a short amount of time.
What are leafhoppers?
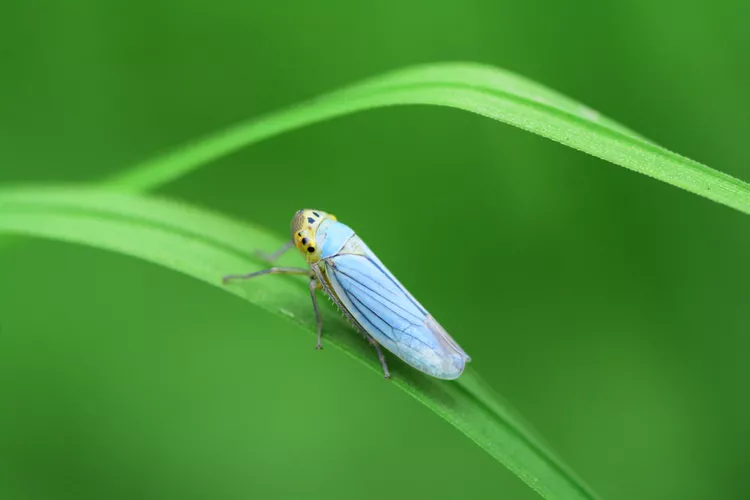
Leafhoppers are small, sap-sucking insects that feed on leaves and stems and may transmit viral diseases to your plants. These insects have short, wedge-shaped bodies that measure no more than half an inch long, depending on the type. You can also recognize leafhoppers by their distinctive patterns of movement. When disturbed, they spring forward or backwards, or may even walk sideways like crabs.
Leafhoppers belong to the Cicadellidae family, which contains over 23,000 species. With all that variety, leafhoppers can look quite different. They can range in color from green to white and yellow and many feature multi-colored patterning to their bodies, which can be vibrant. Both nymphs and adults feed on plant sap; however, only adult leafhoppers have wings.
In a single year, leafhoppers can produce 2 to 3 generations in your garden, although their numbers tend to peak around mid-summer to fall. Adult leafhoppers lay about 6 eggs daily on plant stems and leaves. Eggs and adults may be able to overwinter in garden beds if you live in a location with mild winters.
What do leafhoppers eat?
Leafhoppers aren’t picky insects and they will feed on a wide range of vegetables, herbs, and flowers, including potatoes, corn, beans, and roses. Some varieties of leafhoppers are generalists that will feed on different plants, while others require specific host plant species to live. Common leafhopper varieties you may encounter in your garden include the turf grass leafhopper, the two-spotted leafhopper, and the potato leafhopper.
As leafhoppers feed on your vegetation, their saliva causes a reaction in plant leaves that can result in leaf spotting and stippling, leaf curl, yellowing, or stunted growth. Other signs that leafhoppers have invaded your garden include finding the leafhoppers themselves or discovering their shed exoskeletons on the undersides of affected plant leaves.
How to Prevent Leafhoppers
Leafhoppers are relatively common insects and are naturally found throughout the world. These insects congregate where plants, including weeds, grow. If you’ve experienced a leafhopper infestation in your garden in previous years, there’s a good chance these pests are still around. Take some extra precautions to reduce their impact with these techniques:
- Good garden maintenance. If leafhoppers have damaged plants in your garden in the past, it’s important to clear out all infested vegetation to avoid overwintering insects. Rotating your crops throughout your garden on a 3 to 5 year cycle can also limit leafhopper activity.
- Floating row covers. Set up your floating row covers at the beginning of the growing season to help shield your plants from leafhoppers and other pests. Just be sure to remove the floating row covers occasionally if your plants need to be pollinated by insects in order to set fruit.
- Companion plants. Grow certain companion plants known for their natural pest control abilities near vulnerable crops that leafhoppers like to target. For example, flowering dill, flowering chives, yarrow, and sweet alyssum will attract lacewings, minute pirate bugs, and ladybugs that naturally feed on leafhoppers and will help to keep your garden pest-free.
Many predatory insects can be ordered online if you don’t want to wait for them to find your garden naturally. However, you'll want to grow plants that support these beneficial insects so they stick around after you release them into your garden. And avoid using pesticides that may harm the bugs you want around.
How to Get Rid of Leafhoppers
Just a few leafhoppers won’t cause a lot of damage and they may not need treatment. However, if you’ve noticed a lot of leafhoppers in your garden, you’ll want to act quickly to protect your plants.
Spraying your plants with an organic insecticidal soap or neem oil spray can be an effective way to eliminate both adult leafhoppers and nymphs. Remember to always apply these treatments after the sun sets to avoid issues like sunscald. Plus, bees and other pollinators are less active after dark so less likely to be in harm's way.
Dusting diatomaceous earth, which is made from fossilized diatoms, can also reduce leafhopper populations. However, keep in mind that diatomaceous earth may also affect bees and other beneficial pollinators, so never apply it to plants that are in bloom.